Table of Contents
ToggleHow Much Hair Loss is Normal- 6 Key Facts to Know
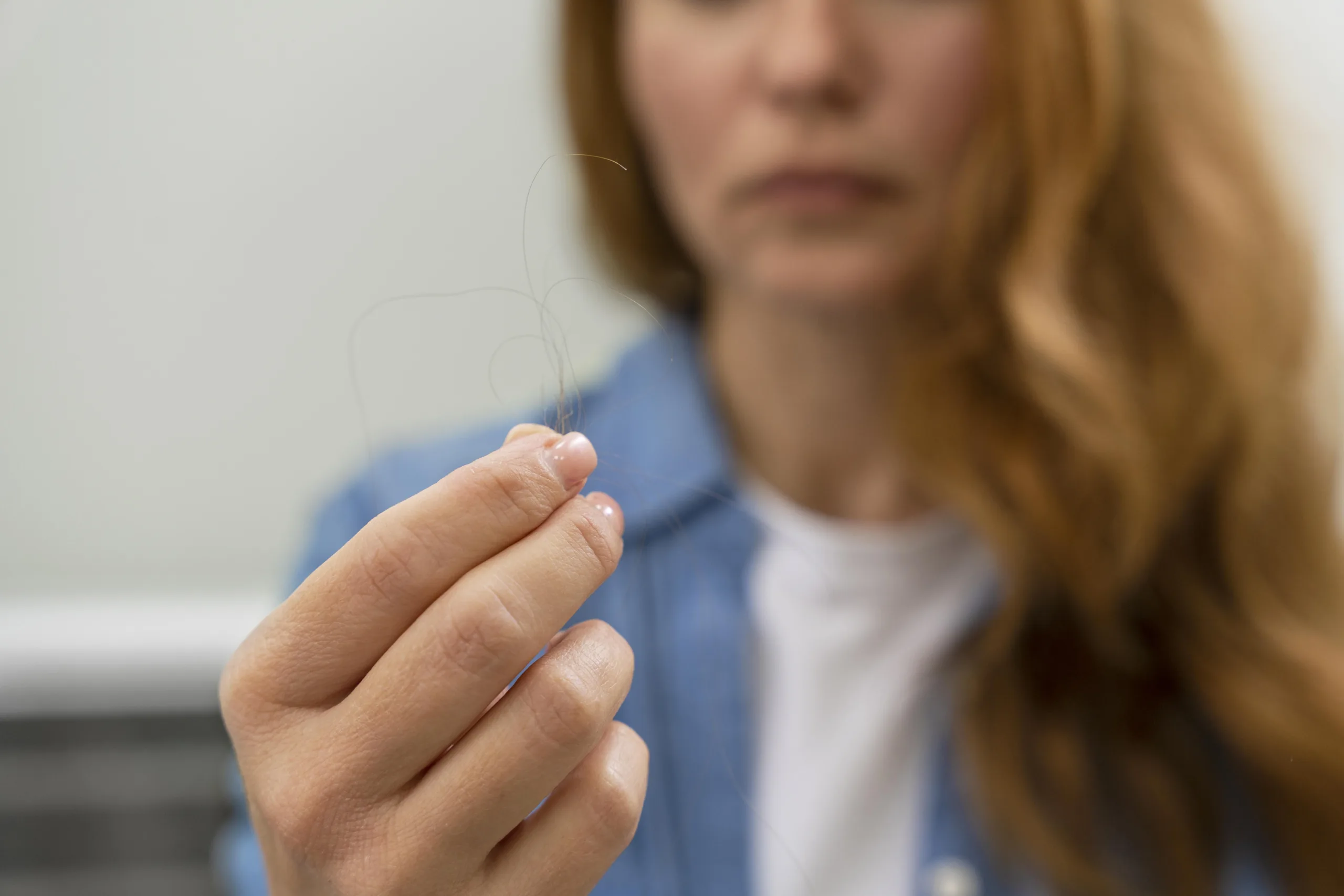
How much hair fall is normal? Hair fall is a common condition for many people, and the amount of hair loss can vary based on factors like age, genetics, certain health conditions, and lifestyle.
Shedding some hair while showering or throughout the day is a normal part of the hair growth cycle.
But how much hair fall is actually normal?

Knowing how much hair loss is normal, helps differentiate between regular hair loss and possible hair loss issues Here’s what you need to know.
Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
To understand normal hair loss, it’s essential to grasp the basics of the hair growth cycle. Exploring how our hair grows involves understanding its cycle of growth. The process can be outlined in three main phases:
- growth (anagen),
- transition (catagen),
- rest (telogen).
During the growth phase, hair actively lengthens from the root. Then comes the transition phase, where growth stops, and the follicle prepares for renewal. Finally, in the resting phase, the old hair sheds to make way for new growth.
This cycle repeats itself continuously, ensuring our hair remains in a state of renewal. Understanding this cycle helps us appreciate the natural rhythm of our hair’s growth and shedding.
But how much hair loss is Normal?
Determining what qualifies as normal hair loss involves understanding the natural shedding process our hair undergoes. It’s typical for people to lose some hair daily as part of the hair growth cycle. Generally, individuals shed between 50 to 100 hairs per day.
which may vary depending on factors like age, genetics, and overall health. However, if hair loss exceeds this range or if there are noticeable changes in hair thickness or scalp coverage, it may indicate a problem.
Monitoring hair loss patterns and considering individual circumstances can help distinguish between normal shedding and excessive hair loss, prompting appropriate action if needed.
Factors Influencing Hair Loss
Several factors can influence the rate of hair loss, including:
Genetic Predisposition
The genetic heritage of a person plays a pivotal role in shaping the patterns of hair loss they may encounter.
Individuals with a genetic predisposition to conditions like male or female pattern baldness are more likely to experience hair loss.
Post-surgery medication
Hair loss can sometimes occur as a side effect of certain potent medications prescribed following a surgical procedure.
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can impact hair growth cycles. Hormonal imbalances may lead to increased hair shedding or thinning.
Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions, including alopecia areata, scalp infections, and autoimmune diseases, can contribute to hair loss.
Treating underlying medical conditions is essential for addressing associated hair loss.
Lifestyle Factors
Stress: Persistent stress has the potential to disturb the natural rhythm of hair growth and play a role in causing hair loss.
Nutrition: Poor diet lacking essential nutrients can weaken hair follicles and lead to increased shedding.
Hair loss in Men
Genetics:
Men may experience hair loss for various reasons. One common cause is genetics, where a family history of baldness can increase the likelihood of hair loss.

Hormonal imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances, especially high levels of a hormone called DHT, can also lead to hair thinning.
Age:
Getting older is another factor, as aging can affect hair growth. Stress, poor diet, and some medical conditions can also play a role in hair loss for men.
Lifestyle:
Certain lifestyle choices like smoking or drinking too much alcohol can make hair loss worse.
Hair Loss in Women
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid imbalances can contribute to hair loss in women.
Genetics: Female-pattern hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, can be inherited and is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair over time.
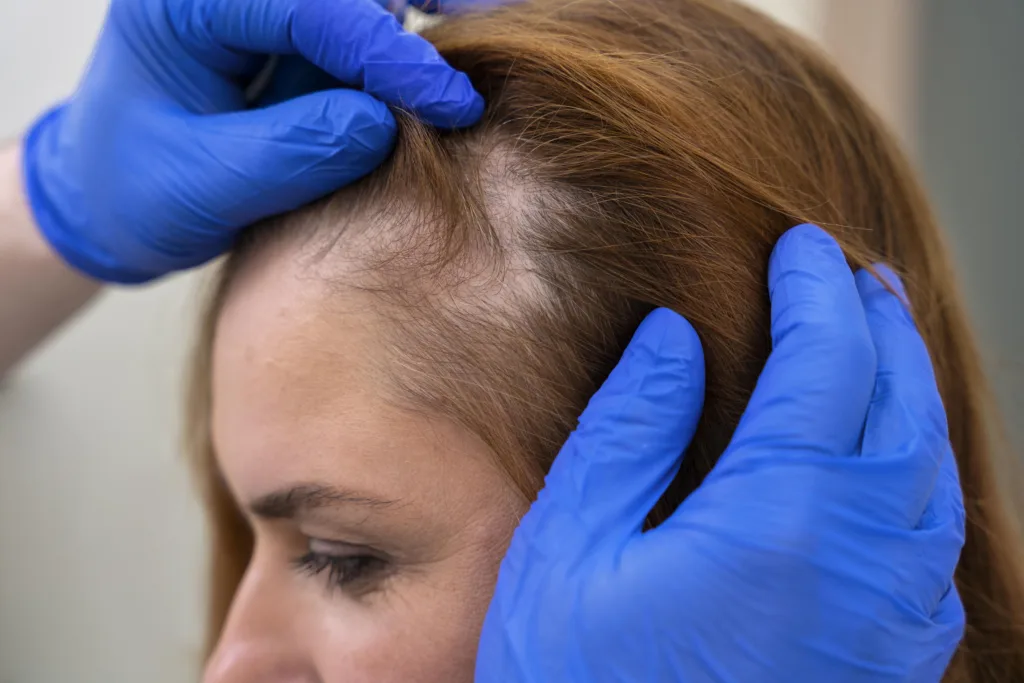
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), autoimmune disorders, and scalp infections can lead to hair loss in women.
Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the resting phase of the hair growth cycle and sheds excessively.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamins D and B12 can affect hair health and contribute to hair loss in women.
Hairstyling Practices: Excessive heat styling, tight hairstyles (like ponytails or braids), and chemical treatments can damage the hair shaft and lead to breakage and hair loss.
Medications: Certain medications, including some birth control pills, blood thinners, and chemotherapy drugs, may cause hair loss as a side effect.
Aging: As women age, the rate of hair growth may slow down, and hair follicles may become less active, resulting in thinner hair.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some hair loss is normal, certain signs may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention. These include:

- Sudden or excessive hair loss
- Noticeable thinning or bald patches
- Hair loss coupled with itching, inflammation, or discomfort.
- Hair loss occurring at a young age or progressing rapidly.
Remember that addressing excessive hair loss may require patience and a combination of approaches tailored to your individual needs. Ask a doctor for personalized advice and treatment suggestions.
Summary
Understanding what constitutes normal hair loss is essential for maintaining hair health and identifying potential issue.
While losing 50 to 100 hairs per day is considered normal for most people, it’s crucial to monitor changes in hair loss patterns and seek medical advice if necessary.
By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure that your hair remains healthy and vibrant for years to come.
Frequently Asked Question's
Q. Is it normal to experience more hair loss during certain seasons or times of the year?
A. Yes, it’s quite common for people to experience seasonal shedding, especially during the fall and spring months.
Q. Can hormonal changes cause hair loss, and is it normal?
A. Yes, hormonal changes can indeed lead to hair loss, and it’s considered normal in certain circumstances. For example, hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause can all affect the hair growth cycle.